Breast Augmentation
Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy.
Breast augmentation procedure steps
Step 1 – Anesthesia
Medications are administered for your comfort during breast augmentation surgery. The choices include intravenous sedation and general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best choice for you.
Step 2 – The incision
Incisions are made in inconspicuous areas to minimize visible scarring. You and your plastic surgeon will discuss which incision options are appropriate for your desired outcome. Incision options include:
Inframammary incision
Transaxillary incision
Periareolar incision
Incisions vary based on the type of implant, degree of enlargement desired, your particular anatomy, and patient-surgeon preference.
Step 3 – Implant choice: Silicone breast implants or saline breast implants?
Breast size and shape are important, so be honest and open about your expectations when talking with your surgeon.
Implant type and size will be determined not just on your desired increase in size but more importantly on your breast anatomy, skin elasticity and body type.
Options for Breast Implants
Saline breast implants are filled with sterile salt water. They can be filled with varying amounts of saline which can affect the shape, firmness and feel of the breast. Should the implant shell leak, a saline breast implant will collapse and the saline will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body.
Silicone breast implants are filled with an elastic gel. The gel feels and moves much like natural breast tissue. If the implant leaks, the gel may remain within the implant shell, or may escape into the breast implant pocket.
A leaking implant filled with silicone gel may not collapse. If you choose these implants, you may need to visit your plastic surgeon regularly to make sure the implants are functioning properly. An ultrasound or MRI screening can assess the condition of breast implants.
Implant manufacturers occasionally introduce new styles and types of implants, so there may be additional options available.
Currently Saline breast implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women 18 years of age and older.
Currently Silicone breast implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women 22 years of age and older.
Saline or silicone implants may be recommended at a younger age if used for reconstruction purposes.
See http://www.breastimplantsafety.org/ for current information.
Step 4 – Inserting and placing the breast implant
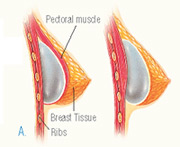
After the incision is made, a breast implant is inserted into a pocket either:
- Under the pectoral muscle (a submuscular placement), or
- Directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle (a submammary/ subglandular placement)
The method for inserting and positioning implants depends on the type of implant, degree of enlargement desired, your body type, and your surgeon’s recommendations.
Step 5 – Closing the incisions
Incisions are closed with layered sutures in the breast tissue and with sutures, skin adhesive or surgical tape to close the skin. Over time the incision lines will fade.

Step 6 – See the results
The results of breast augmentation surgery are immediately visible. Over time, post-surgical swelling will resolve and incision lines will fade. Satisfaction with your new image should continue to grow as you recover and realize the fulfillment of your goal for fuller breasts.





